In the ever-evolving landscape of e-commerce, where every click counts, your website’s visibility on search engines like Google is paramount — considering how organic search is the primary source of traffic and revenue for e-commerce websites.
And that visibility largely depends on how Googlebot — the web crawler used by Google to gather the information needed to build a searchable index of the web — navigates your website to crawl and index its pages. If there are issues in crawlability or indexability, your e-commerce site or its important pages may not rank optimally or even become invisible on the SERP.
Thus, you need to think of Googlebot as your primary customer, because understanding its journey and behavior is the key to outranking your competitors. That’s where technical SEO and crawl budget optimization comes into the picture. The flowchart below illustrates how your e-commerce pages get crawled and indexed by Googlebot, and then ultimately ranked.
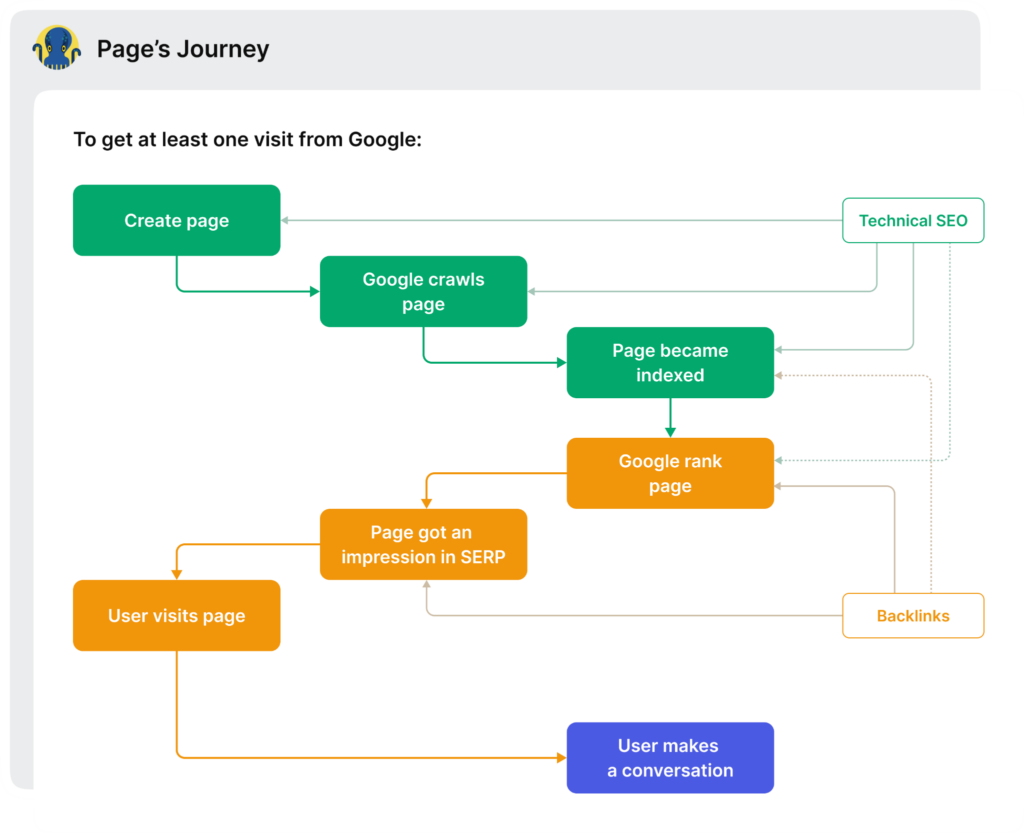
In this post, you’ll learn how to understand Googlebot’s behavior, make friends with Google and outperform your competitors on Google search results.
1. Optimize Crawl Budget
Just like a store manager needs to allocate shelf space wisely, Google allocates a finite amount of time and resources (i.e. budget) to crawl your website. Wasting this crawl budget on unimportant pages can hinder the indexing of vital content.
Thus, you need to know exactly where the Googlebot goes on your e-commerce website, where it does not, and what to change. For this, performing a log file analysis helps uncover vital aspects like:
- Crawling frequency
- Pages being visited and crawled
- Crawl budget waste (spent on Orphaned pages that are not in site structure)
- Pages ignored by Googlebot
- Slow-loading pages (which not only hurts the UX but also consumes more crawl budget)
Armed with this data, ensure that:
- Your cornerstone content, product pages, and key categories are accessible and well-structured.
- You don’t allow crawling to pages with “infinite” results, like an infinite product search results page. Block them with robots.txt or nofollow tags.
- You trim the excess by deleting duplicate, thin, irrelevant, and low-value content. This streamlines the crawl process and enables Googlebot to focus on what truly matters.
- You aim for a load time between 500 milliseconds to 2 seconds to enable an efficient crawling and indexing process. Use Google PageSpeed Insights to understand your page load time and get guidance on how to fix your site’s speed and Core Web Vitals.
Furthermore, factors like the distance from index (DFI) and the internal linking structure strongly influence which pages are prioritized by crawlers. That is, pages closer to the homepage and ones with a higher number of quality internal links are more likely to be crawled frequently. Conversely, pages buried deep in the site structure or with few internal links would see far fewer Googlebot visits.
2. Visualize Googlebot Behavior on Your Website
Googlebot’s journey through your website is not random; it follows patterns and algorithms. Visualizing this behavior allows you to anticipate its actions and tailor your site accordingly.
When you know where Googlebot spends its time, you can make informed decisions to enhance the indexability of essential pages, ensuring they are prioritized for crawling and indexing.
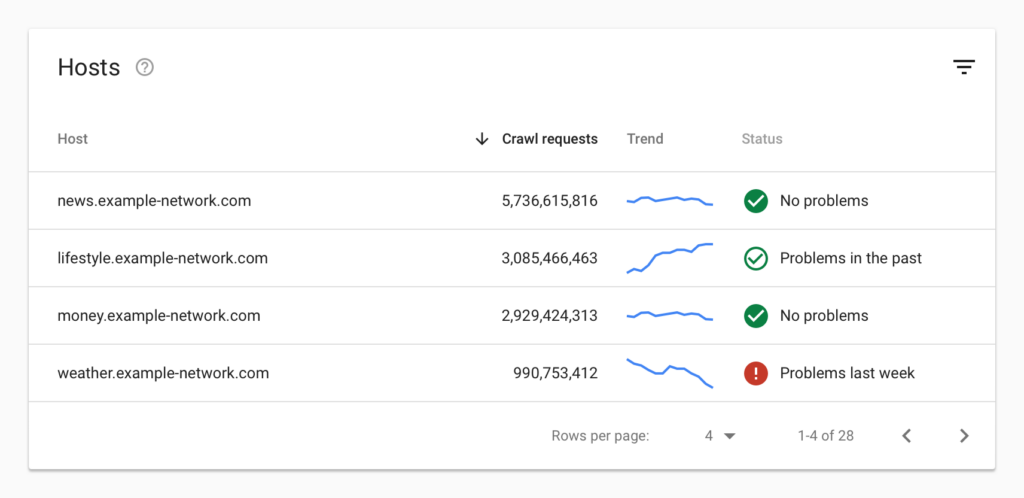
Tools like Google Search Console (GSC) can help you gain insights into Googlebot’s crawling behavior. For instance, the Crawl Stats report shows how many requests were made and when, what your site’s server response was, and any issues faced. You can use this report to detect whether Google encounters serving problems when crawling your site.
But it shows just general trends, without the possibility to dive deeper into categories, or page level. That’s the field where log analysis helps to get the proper insights for further optimization.
3. Use the Insights to Multiply Positive Results
Gaining insights into Googlebot’s behavior through log file analysis and GSC visualization is not just about collecting data — it’s about turning that data into actionable and recurring improvements for your e-commerce site.
Looking at your site’s logs and visual data, pinpoint technical SEO issues that might be hindering your site’s performance. Whether it’s addressing crawl errors, optimizing site speed, reorganizing your site structure, or resolving indexability issues, insights from tools like log analyzers and Google Search Console guide you in making precise fixes and determining the most effective pages of your site.
For instance, when you identify and rectify crawl errors, you can ensure that critical product pages are crawlable to maximize the visibility of your products and thus boost sales and revenue. When you speed up your e-commerce site by optimizing images, leveraging browser caching, and using Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), those faster loading times translate into a better user experience and reduced bounce rates, thus increasing the likelihood of converting visitors into customers — directly impacting sales and revenue. And when you streamline and reorganize your site’s structure to enhance user navigation, you make it easier for customers to find products and ensure that search engines can crawl and index your pages effectively, again contributing to increased sales and revenue.
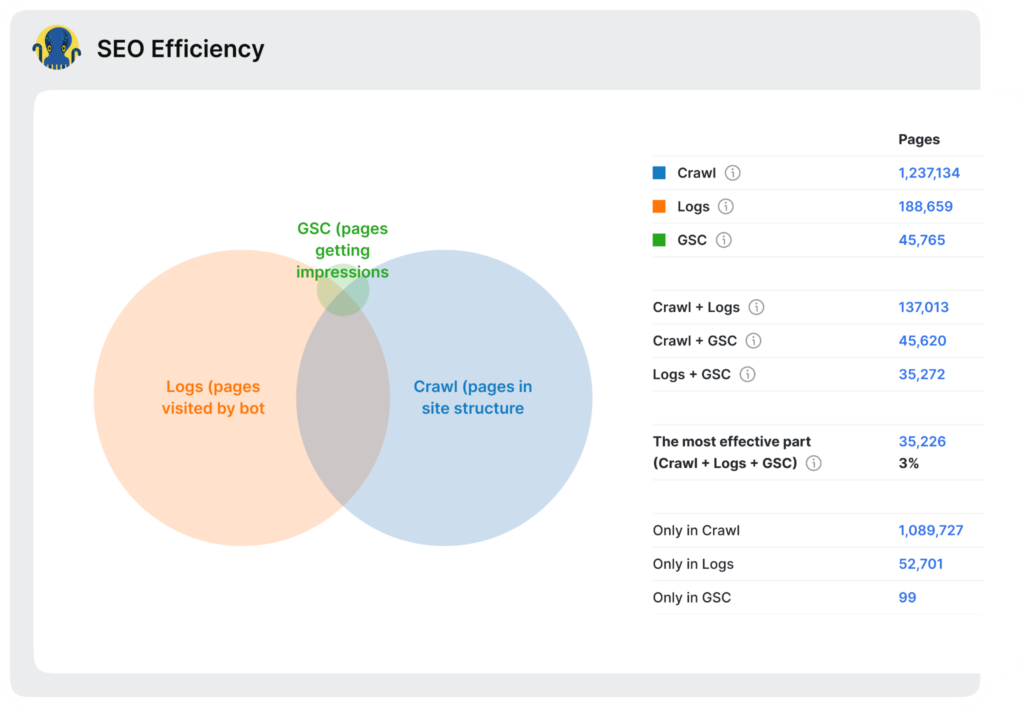
To assess the impact of your technical SEO fixes, it’s crucial to establish a baseline by measuring relevant metrics before implementing changes. Track key indicators such as crawl ratio, indexation status, Googlebot’s visits, organic traffic, and keyword rankings.
Then, with a log analyzer like JetOctopus, you can head over to the Impact section to see what fixes (such as fixing orphaned pages or crawl budget waste) would have the greatest impact specifically for your e-commerce website.
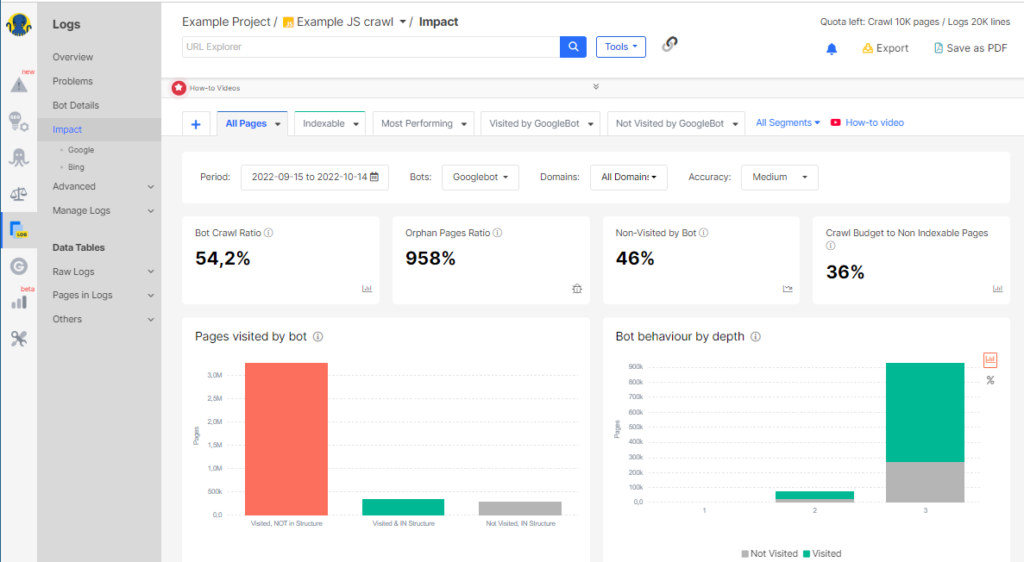
This way, you take action based on the data, implement changes, and check your overall SEO performance again, thus having a better understanding of what’s improved. So, after implementing fixes, compare metrics to gauge the effectiveness of your optimizations.
Ultimately, effective SEO is an iterative process. Focus on problem areas identified through your insights and make continual improvements. Frequently monitor the data, make tweaks, and track progress. This iterative approach leads to gradual but substantial improvements in site visibility over the course of a few months.
Conclusion
By using insights derived from log file analysis and Googlebot visualization, you can now transform raw data into a roadmap for your e-commerce website optimization.
It’s not just about getting noticed by Google; it’s about staying relevant and growing sustainably in the highly competitive e-commerce landscape. This strategic approach allows you to multiply positive results, ultimately outperforming competitors and achieving long-term success. It makes your SEO visualized, predictable and growing!






